China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News. This headline isn’t hyperbole; China’s manufacturing dominance is a global reality shaped by decades of strategic planning, massive investment, and a relentless drive for efficiency. This exploration delves into the history of this rise, examining the key factors that propelled China to its current position, the challenges it faces, and what the future might hold for this manufacturing behemoth.
We’ll trace China’s manufacturing journey, comparing its growth to that of other industrial giants. We’ll dissect the strengths of its ecosystem – from low labor costs to advanced supply chains – and analyze its vulnerabilities, including trade tensions and environmental concerns. Finally, we’ll project potential future scenarios, considering the impact of automation and global competition.
China’s Manufacturing Dominance

China’s rise as a manufacturing superpower is a remarkable story of economic transformation, fueled by strategic policy decisions, a massive workforce, and a relentless focus on industrial growth. This journey, however, is not without its complexities and challenges, and understanding its trajectory is crucial for comprehending the global economic landscape.
China’s Manufacturing Dominance: Historical Context
China’s manufacturing sector’s evolution is a multi-decade process marked by significant policy shifts and technological advancements. From a largely agrarian economy in the early 20th century, China gradually embraced industrialization, accelerating significantly after its economic reforms began in 1978. This period saw the establishment of Special Economic Zones (SEZs), attracting foreign investment and fostering export-oriented manufacturing. The country’s entry into the World Trade Organization (WTO) in 2001 further propelled its integration into the global manufacturing network.
That Hacker News thread about China’s manufacturing dominance got me thinking – a lot of those products rely on software. If you want to be part of that tech ecosystem, check out this resource on affordable full stack developer bootcamps with job placement to upskill. Knowing how to build the software that runs these global supply chains is a seriously valuable skill in today’s world, especially considering China’s continued influence.
Comparing China’s rise with other manufacturing powerhouses reveals distinct patterns. The UK’s dominance was rooted in the Industrial Revolution, leveraging its early technological advancements and vast colonial empire. The US capitalized on technological innovation and mass production techniques during the 20th century. Japan’s post-war economic miracle was fueled by efficient manufacturing processes and a focus on quality. China’s ascent, however, is unique in its scale and speed, leveraging a massive population and strategic government planning.
| Country | Year of Peak Manufacturing Output (Approximate) | GDP per capita (USD, Approximate at Peak) | Manufacturing Employment Percentage (Approximate at Peak) |
|---|---|---|---|
| United Kingdom | 1910s | Relatively low, due to limitations in data availability. | High, likely exceeding 30% |
| United States | 1960s | High, reflecting strong post-war economic growth. | Significant, around 25-30% |
| Japan | 1980s | Substantially increased from post-war levels. | High, reflecting industrial focus. |
| China | 2010s – Present | Significantly increased since 1978. | High, though decreasing recently. |
Strengths of China’s Manufacturing Ecosystem
China’s manufacturing prowess stems from a confluence of factors. Low labor costs historically provided a significant competitive advantage, attracting global manufacturers. The vast domestic market ensures substantial demand for manufactured goods, further driving production. Robust supply chains, often vertically integrated, ensure efficient production and delivery. Government policies, including infrastructure development and export promotion, have been instrumental in fostering this ecosystem.
Technological advancements, while still a work in progress, are increasingly impacting China’s manufacturing capabilities. The government’s push towards “Made in China 2025” aims to enhance technological self-reliance and upgrade its industrial base. Specific industries like electronics, textiles, and renewable energy demonstrate China’s manufacturing dominance.
So you’re curious about China’s manufacturing dominance? The Hacker News discussion, China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News , offers some great insights. It dives into the reasons behind China’s massive manufacturing output and its global impact. Check it out to get a better grasp on this crucial topic.
Challenges and Weaknesses in China’s Manufacturing Sector, China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News
Despite its strengths, China’s manufacturing sector faces significant challenges. Over-reliance on exports makes it vulnerable to global economic fluctuations and trade disputes. Environmental concerns related to pollution and resource depletion are increasingly pressing. Rising labor costs are eroding its cost advantage. Intellectual property rights protection remains a concern, impacting technological innovation.
- Diversifying export markets to reduce dependence on any single region.
- Investing heavily in cleaner production technologies and stricter environmental regulations.
- Upgrading skills and increasing automation to offset rising labor costs.
- Strengthening intellectual property rights protection and fostering a culture of innovation.
The Future of China’s Manufacturing Superpower Status
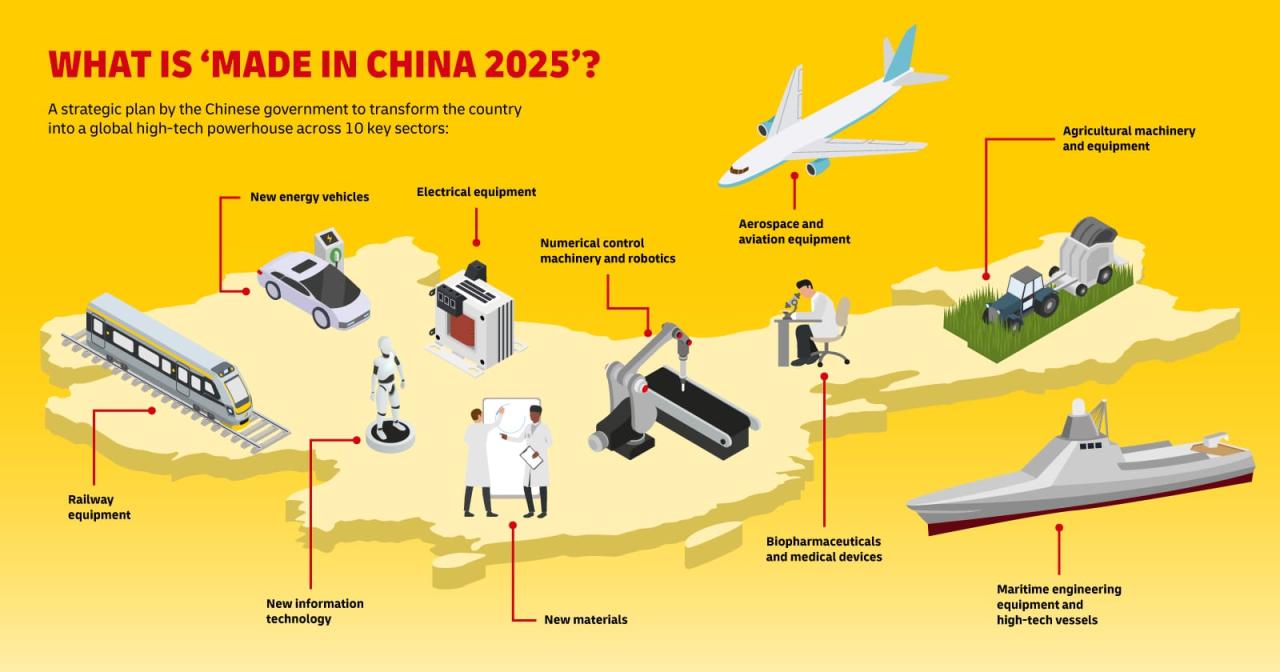
China’s continued dominance in manufacturing is not guaranteed. Emerging economies present competition, and technological advancements, particularly automation and AI, will reshape the sector. While China is investing heavily in automation, its success will depend on its ability to adapt and innovate. A hypothetical scenario in 2040 could see China maintaining its manufacturing output, but with a greater emphasis on high-value-added products and advanced technologies, possibly shifting towards a more service-oriented economy alongside its manufacturing base, mirroring the transformation seen in other advanced economies.
Global Implications of China’s Manufacturing Power
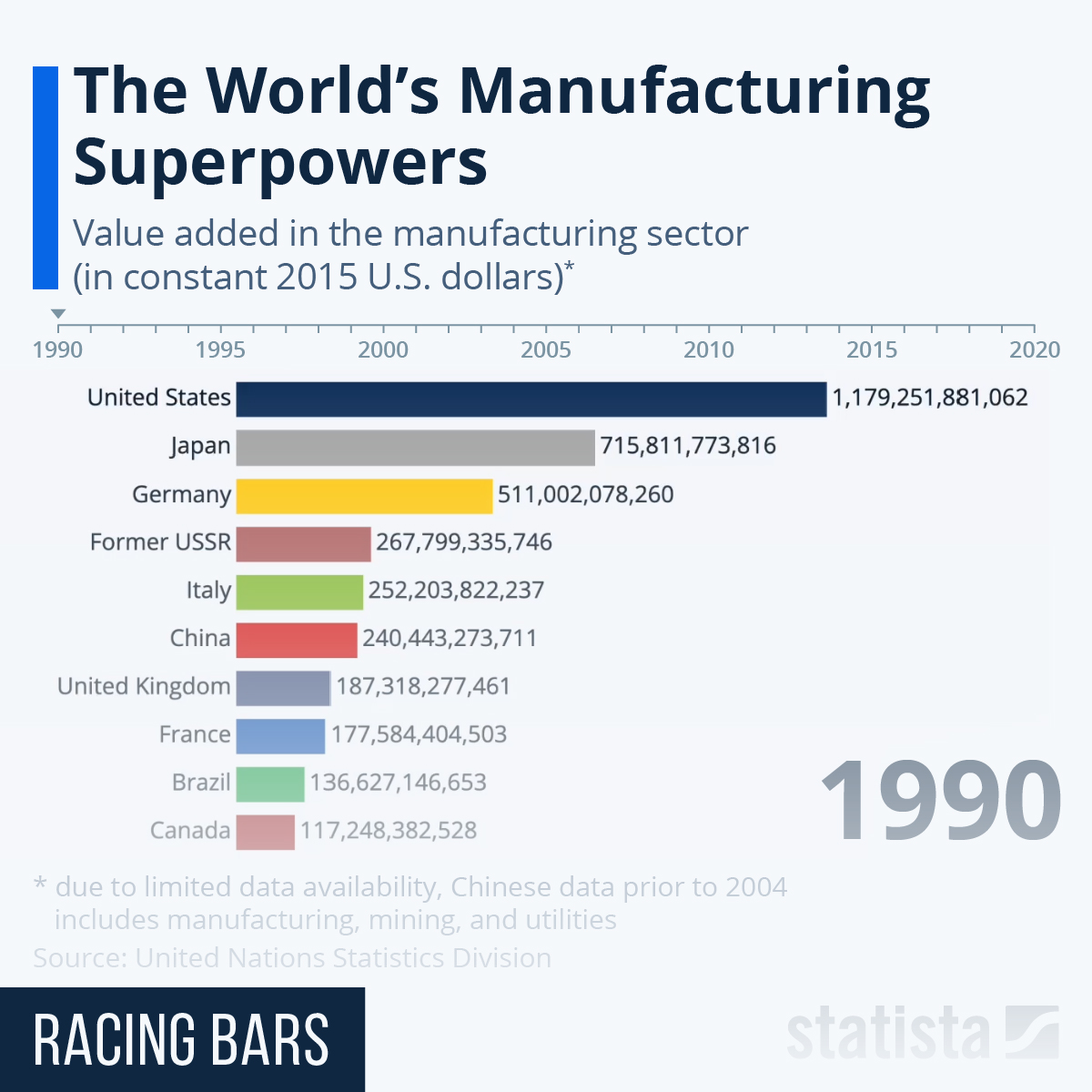
China’s manufacturing dominance profoundly impacts global supply chains and trade. It has lowered the cost of many goods, benefiting consumers worldwide. However, it has also raised concerns about job displacement in other countries and the potential for economic imbalances. The global distribution of manufacturing output is heavily skewed towards China, though other nations are striving to increase their share.
So, you’re reading about China’s manufacturing dominance on Hacker News – a fascinating topic, right? It makes you think about the global economy’s interconnectedness. For example, consider the stark contrast: while China churns out goods, a football player like Jermaine Burton faces a very different kind of challenge, as seen in this news story: Jermaine Burton left home by Bengals, gets eviction notice.
It highlights how even within a globalized system, individual struggles persist, reminding us that the macro and micro always intertwine. This brings us back to China’s manufacturing power – a force shaping those individual realities in many ways.
| Country | Manufacturing Output (USD, Approximate) | Percentage of Global Manufacturing Output (Approximate) | Key Export Industries |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | Trillions of USD | ~30% | Electronics, textiles, machinery, etc. |
| United States | Trillions of USD | ~15% | Aerospace, pharmaceuticals, automobiles, etc. |
| Germany | Hundreds of billions of USD | ~5% | Automobiles, machinery, chemicals, etc. |
Outcome Summary

China’s manufacturing dominance is undeniable, a testament to decades of strategic planning and execution. While challenges remain – rising labor costs, geopolitical uncertainties, and environmental concerns – China’s sheer scale and adaptability suggest continued influence on the global manufacturing landscape. The future likely holds a blend of continued growth, technological advancement, and a shift towards higher-value manufacturing, solidifying its place as a key player in the global economy for years to come.
Understanding this evolution is crucial for navigating the complexities of the modern global marketplace.
Questions and Answers: China Is The Manufacturing Superpower | Hacker News
What are the biggest threats to China’s manufacturing dominance?
Rising labor costs, increasing automation in competing nations, trade wars, and environmental regulations are significant threats.
How does China’s manufacturing sector impact consumers globally?
It leads to lower prices for many goods, increased availability of products, and influences global supply chains, impacting product availability and pricing worldwide.
What role does technology play in China’s manufacturing future?
Automation, AI, and advanced manufacturing techniques are crucial for maintaining competitiveness and moving towards higher-value production.
Is China’s manufacturing sector sustainable in the long term?
Its long-term sustainability depends on addressing environmental concerns, investing in innovation, and adapting to changing global dynamics.
