How to operate a drone safely and effectively is crucial for both beginners and experienced pilots. This guide provides a structured approach to mastering drone operation, covering everything from pre-flight checks and safety protocols to advanced flight techniques and troubleshooting common issues. We’ll explore the intricacies of drone controls, various flight modes, optimal camera settings for stunning aerial photography, and essential maintenance procedures to ensure the longevity of your drone.
Prepare to take flight with confidence!
From understanding airspace regulations and navigating different terrains to capturing breathtaking aerial footage, this comprehensive guide equips you with the knowledge and skills necessary to become a proficient drone pilot. We’ll delve into the practical aspects of drone operation, offering clear explanations and step-by-step instructions to ensure you can confidently and safely operate your drone. We will also cover essential maintenance and troubleshooting tips to keep your drone in top condition.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures

Before embarking on any drone flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to safety procedures are paramount. This ensures both the safe operation of the drone and the safety of those around you. Ignoring these steps can lead to accidents, damage to property, and legal repercussions.
Pre-Flight Drone Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection is crucial for identifying potential issues before takeoff. This minimizes the risk of malfunctions during flight. The following table Artikels key areas to check:
| Item | Check | Action Required | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for cracks, damage, or looseness. | Replace damaged propellers. Tighten loose propellers. | Ensure all propellers are securely fastened. |
| Battery | Check battery level and condition. | Charge battery if necessary. Replace damaged or swollen batteries. | Always use manufacturer-recommended batteries. |
| Camera | Verify camera functionality and lens clarity. | Clean the lens if necessary. | Check for proper image stabilization. |
| GPS Signal | Confirm a strong GPS signal. | Relocate to an area with better GPS reception if necessary. | Sufficient satellites are needed for accurate positioning. |
| Gimbal | Check gimbal movement and stability. | Calibrate the gimbal if necessary. | Ensure smooth and accurate camera movement. |
| Flight Controller | Ensure all connections are secure. | Tighten any loose connections. | Check for any signs of damage. |
Local Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Understanding and complying with local regulations and airspace restrictions is non-negotiable. These regulations vary by location and are designed to ensure safe and responsible drone operation. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines or even legal action. Always check with your local aviation authority before flying.
Safety Precautions During Drone Operation
Prioritizing safety during drone operation is essential. The following precautions should be consistently observed:
- Maintain visual line of sight with the drone at all times.
- Avoid flying near people, animals, or structures.
- Never fly in adverse weather conditions (strong winds, rain, snow).
- Be mindful of surrounding airspace and avoid flying near airports or other restricted areas.
- Respect privacy and avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Always have a backup plan in case of unexpected issues.
Handling Unexpected Situations During Flight
A flowchart can aid in decision-making during unexpected flight situations. This visual guide helps to quickly assess the situation and take appropriate action.
(A detailed flowchart would be included here, illustrating decision points based on the nature of the problem (e.g., low battery, GPS loss, loss of control) and the corresponding actions (e.g., return to home, emergency landing, power off). The flowchart would guide the user through a logical sequence of steps to mitigate the issue.)
Drone Controls and Navigation: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding drone controls and navigation techniques is crucial for safe and effective operation. Different drones offer varying control mechanisms and navigation features.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation, ultimately leading to a rewarding flying experience.
Drone Control Mechanisms
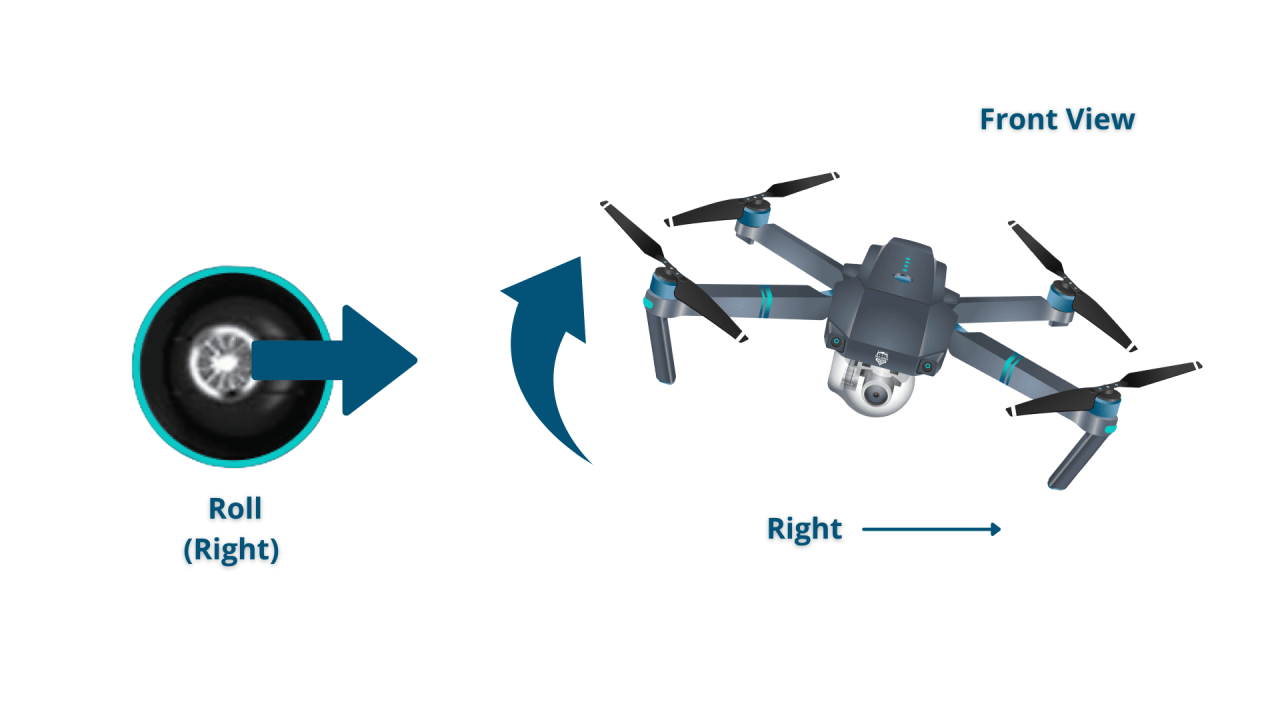
Most drones utilize either joysticks or touchscreen controls, or a combination of both. Joysticks offer precise control over movement, while touchscreens provide intuitive access to various flight modes and camera settings. Joysticks provide more direct control, especially in challenging environments, while touchscreens offer ease of use for beginners. The best choice depends on personal preference and experience level.
Compass and Sensor Calibration
Calibrating the drone’s compass and sensors is essential before each flight. This ensures accurate positioning and stable flight. The calibration process typically involves a series of movements as instructed by the drone’s software, which helps the drone accurately orient itself and adjust for any magnetic interference.
GPS Navigation
Utilizing GPS coordinates and waypoints enhances navigation precision and enables automated flight paths. This is particularly helpful for complex aerial photography or videography projects.
- Setting Waypoints: Most drone software allows you to define a series of GPS coordinates (waypoints) that the drone will automatically follow.
- GPS-Assisted Flight: The drone uses GPS signals to maintain its position and altitude, allowing for smoother and more stable flight.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): The drone can automatically return to its takeoff point using GPS data, a crucial safety feature.
Maneuvering in Various Environments
Effective drone maneuvering requires adapting techniques to different environments. Flying in windy conditions necessitates precise control inputs to counteract wind gusts. In tight spaces, slower and more deliberate movements are essential to avoid collisions. Practice is key to mastering these skills.
Flight Modes and Features
Drones offer various flight modes and advanced features to enhance the flying experience and cater to different skill levels. Understanding these modes and features is key to unlocking the full potential of your drone.
Common Flight Modes, How to operate a drone
Several flight modes are common among consumer drones, each designed for a specific purpose or skill level.
- Beginner Mode: Limits speed and responsiveness, ideal for new pilots.
- Sport Mode: Unlocks full speed and agility, suitable for experienced pilots.
- Follow Me Mode: The drone automatically follows a designated subject.
- Waypoint Mode: The drone autonomously follows a pre-programmed path.
- Circle Mode: The drone orbits a chosen point.
Advanced Drone Features
Advanced features enhance flight safety and creative capabilities. Obstacle avoidance systems automatically detect and avoid obstacles, preventing collisions. Return-to-home (RTH) functionality ensures the drone safely returns to its takeoff point in case of signal loss or low battery.
Camera Settings
Understanding camera settings is crucial for capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos. Different settings impact image quality and file size.
| Setting | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resolution | Image size (e.g., 4K, 1080p) | Higher detail and clarity | Larger file sizes, increased storage requirements |
| Frame Rate | Frames per second (fps) | Smoother video, slow-motion capabilities | Larger file sizes, increased processing demands |
| ISO | Sensitivity to light | Better performance in low-light conditions | Increased noise (grain) in images |
Utilizing GPS for Return to Home
The GPS-enabled Return-to-Home (RTH) feature is a critical safety mechanism. To utilize this feature, ensure a strong GPS signal is present before takeoff. Activate the RTH function through the drone’s control interface, and the drone will autonomously navigate back to its starting point. It will usually land in the same location it took off from.
Battery Management and Maintenance
Proper battery care is vital for maximizing battery lifespan and ensuring safe drone operation. Neglecting battery maintenance can lead to reduced flight time, performance issues, and even potential safety hazards.
Battery Care and Storage
Storing batteries at optimal temperatures, avoiding overcharging, and preventing deep discharges are key to prolonging their life. Always store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for proper storage and charging.
Charging and Replacing Batteries
Always use the manufacturer-recommended charger and follow the charging instructions carefully. Never leave batteries unattended while charging. When replacing batteries, ensure the connection is secure to avoid power interruptions during flight.
Signs of a Failing Battery
Signs of a failing battery include reduced flight time, overheating, swelling, or unusual behavior. If any of these signs are observed, replace the battery immediately to avoid potential safety risks.
Routine Drone Maintenance Checklist
Regular maintenance extends the lifespan of your drone and ensures optimal performance. A simple checklist can help maintain a consistent cleaning and inspection schedule.
- Inspect propellers for damage.
- Clean the drone body and camera lens.
- Check all connections for security.
- Inspect the gimbal for smooth movement.
- Check the battery for any signs of damage or wear.
Photography and Videography with a Drone
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding both technical aspects and compositional principles. Mastering these skills unlocks the full creative potential of your drone.
Tips and Techniques for High-Quality Aerial Media
Several techniques can enhance the quality of your aerial footage. Experiment with different shooting modes, camera angles, and lighting conditions to find what works best for your projects. Smooth, deliberate movements are key to avoiding shaky footage.
| Shooting Mode | Description | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Photo | Still image capture | Landscapes, architecture, detailed shots |
| Video | Moving image capture | Timelapses, cinematic shots, aerial tours |
| Timelapse | Series of photos taken over time, compiled into a video | Showing changes over time, creating dynamic sequences |
| Slow Motion | High frame rate video for slow-motion effects | Capturing action, emphasizing details |
Composition Principles
Applying basic composition principles like the rule of thirds, leading lines, and symmetry can greatly enhance the visual appeal of your aerial footage. These techniques guide the viewer’s eye and create a more engaging visual experience.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of regulations and safety procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including practical tips and legal considerations, please refer to this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Ultimately, responsible and safe drone operation hinges on thorough preparation and continuous learning.
Creating Specific Effects
Drones allow for unique effects such as timelapses, which condense long periods into short, dynamic videos, and cinematic shots, using smooth movements and strategic camera angles to create a professional look.
Sample Shot List for a Short Aerial Video

A well-planned shot list ensures a cohesive and engaging final product. The list should detail camera angles, movements, and the desired effect for each shot.
(A sample shot list would be included here, outlining specific shots, camera angles (e.g., high angle, low angle, tracking shot), and desired movements (e.g., slow pan, quick zoom) for a short aerial video project.)
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Despite careful preparation, drone malfunctions can occur. Knowing how to troubleshoot common issues saves time and prevents potential damage. A systematic approach to troubleshooting is essential for efficient problem-solving.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Solutions
Several common drone malfunctions and their solutions are listed below. These solutions should be attempted in order, from simplest to more complex.
- Low Battery Warning: Land the drone immediately and charge the battery.
- GPS Signal Loss: Relocate to an area with better GPS reception or wait for the signal to improve.
- Motor Failure: Inspect the motor for damage and replace if necessary.
- Controller Connectivity Issues: Check the connection between the drone and controller, ensuring the controller’s battery is charged, and the frequencies are correctly matched. Restart the drone and controller if needed.
Troubleshooting Connectivity Problems
Connectivity issues are common. First, ensure the controller’s battery is fully charged and that the drone and controller are within range. Restart both devices and check for any interference from other electronic devices.
Basic Repairs and Maintenance
Simple repairs such as tightening loose screws or cleaning the drone body can often resolve minor issues. Always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for guidance on performing any repairs.
Contacting Customer Support
For complex issues beyond basic troubleshooting, contact the manufacturer’s customer support for assistance. They can provide expert guidance and support for resolving more challenging problems.
Mastering drone operation involves a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical application. By diligently following the pre-flight checklists, understanding drone controls, and mastering various flight modes, you can confidently navigate the skies. Remember to prioritize safety, adhere to regulations, and continuously refine your skills to capture stunning aerial visuals. Safe and happy flying!
Answers to Common Questions
What is the best drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners, often featuring simplified controls and automated features. Research models known for their ease of use and consider factors like flight time and camera quality.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrating your drone’s compass before each flight is recommended, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced any significant impacts.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If your drone loses GPS signal, immediately switch to manual control and attempt to fly it back to your location. If this is not possible, engage the Return-to-Home (RTH) function if available.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies significantly depending on the model, flight conditions (wind, temperature), and usage (camera operation, flight mode). Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
